Intro to Visualizations
Daniel Anderson
Week 2, Class 1
1 / 81
Empirical examples
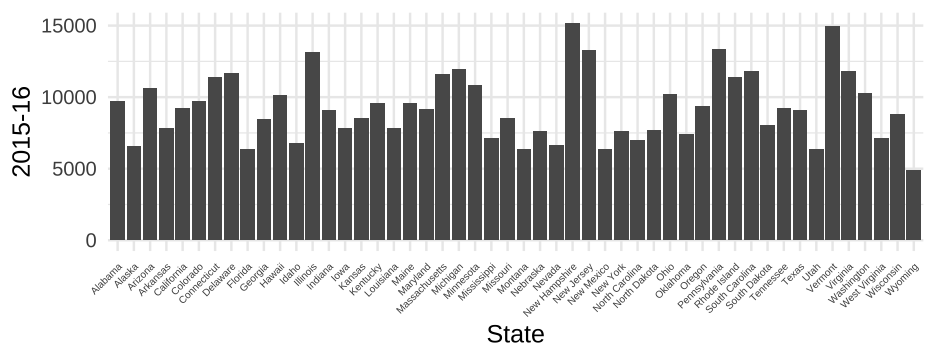
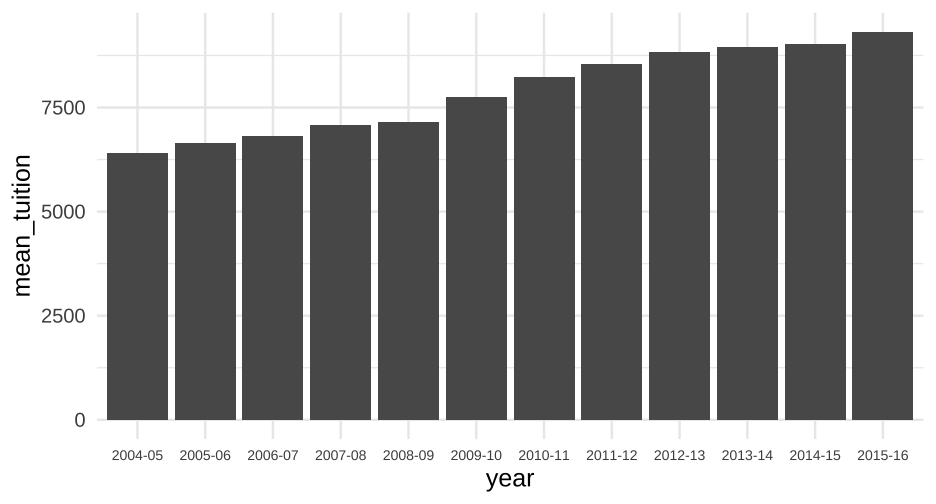
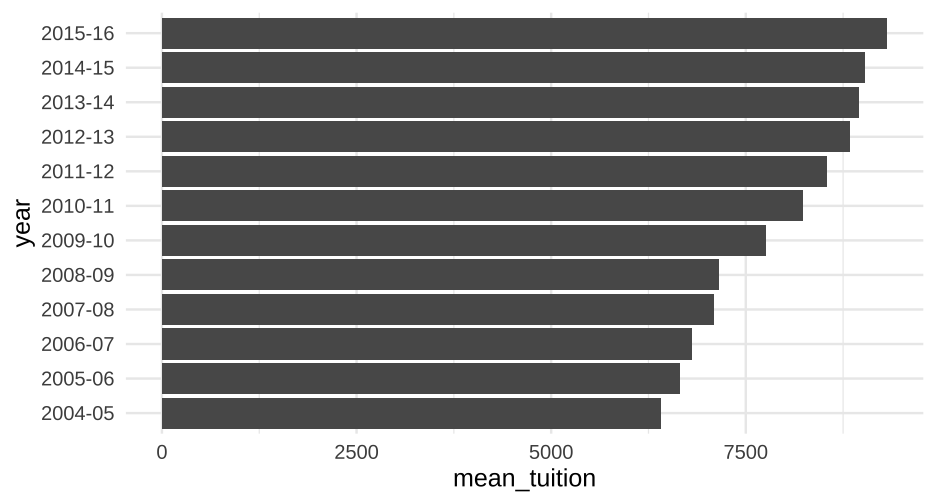
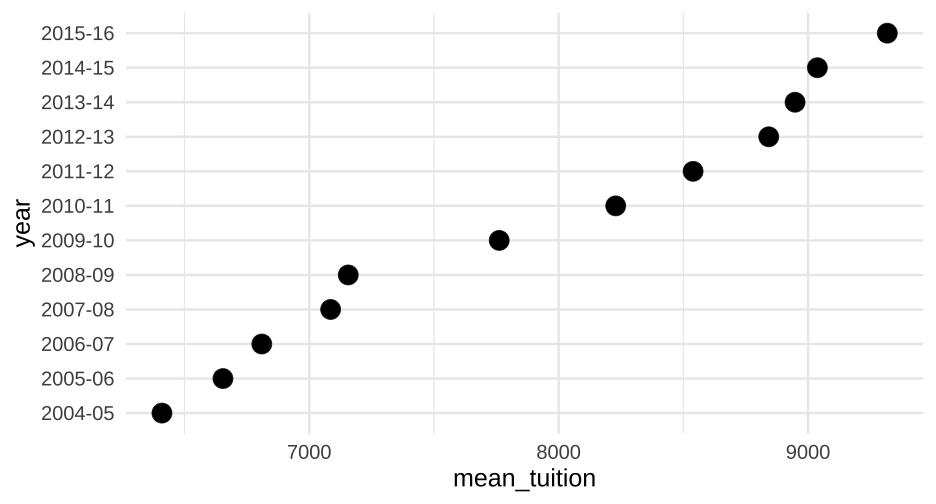
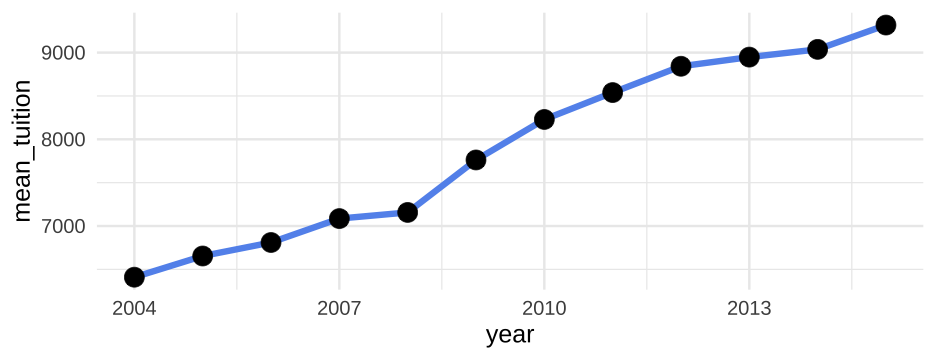
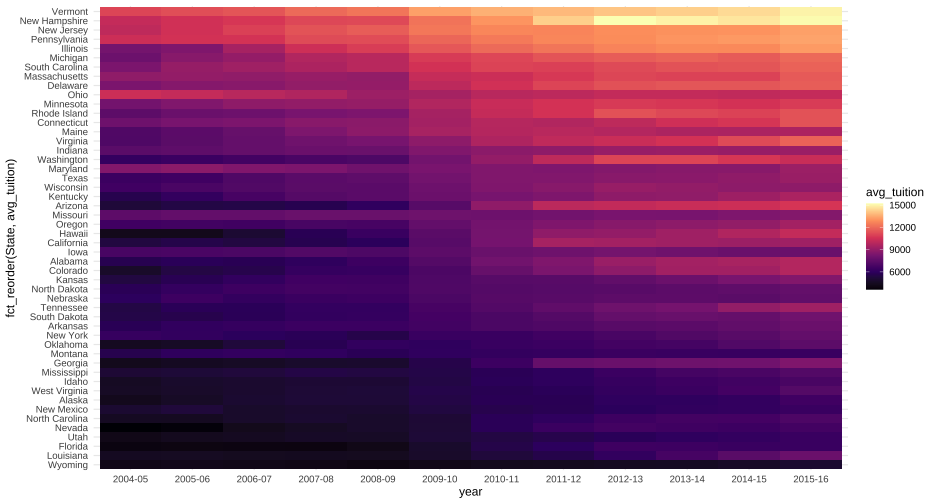
How much does college cost?
library(here)library(rio)tuition <- import(here("data", "us_avg_tuition.xlsx"), setclass = "tbl_df")head(tuition)## # A tibble: 6 x 13## State `2004-05` `2005-06` `2006-07` `2007-08` `2008-09` `2009-10`## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 5682.838 5840.550 5753.496 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954## 2 Alaska 4328.281 4632.623 4918.501 5069.822 5075.482 5454.607## 3 Arizona 5138.495 5415.516 5481.419 5681.638 6058.464 7263.204## 4 Arkansas 5772.302 6082.379 6231.977 6414.900 6416.503 6627.092## 5 California 5285.921 5527.881 5334.826 5672.472 5897.888 7258.771## 6 Colorado 4703.777 5406.967 5596.348 6227.002 6284.137 6948.473## # … with 6 more variables: `2010-11` <dbl>, `2011-12` <dbl>,## # `2012-13` <dbl>, `2013-14` <dbl>, `2014-15` <dbl>, `2015-16` <dbl>46 / 81
Averages tuition by year
How?
head(tuition)## # A tibble: 6 x 13## State `2004-05` `2005-06` `2006-07` `2007-08` `2008-09` `2009-10`## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 5682.838 5840.550 5753.496 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954## 2 Alaska 4328.281 4632.623 4918.501 5069.822 5075.482 5454.607## 3 Arizona 5138.495 5415.516 5481.419 5681.638 6058.464 7263.204## 4 Arkansas 5772.302 6082.379 6231.977 6414.900 6416.503 6627.092## 5 California 5285.921 5527.881 5334.826 5672.472 5897.888 7258.771## 6 Colorado 4703.777 5406.967 5596.348 6227.002 6284.137 6948.473## # … with 6 more variables: `2010-11` <dbl>, `2011-12` <dbl>,## # `2012-13` <dbl>, `2013-14` <dbl>, `2014-15` <dbl>, `2015-16` <dbl>57 / 81
Rearrange
tuition %>% pivot_longer(`2004-05`:`2015-16`, names_to = "year", values_to = "avg_tuition")## # A tibble: 600 x 3## State year avg_tuition## <chr> <chr> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 2004-05 5682.838## 2 Alabama 2005-06 5840.550## 3 Alabama 2006-07 5753.496## 4 Alabama 2007-08 6008.169## 5 Alabama 2008-09 6475.092## 6 Alabama 2009-10 7188.954## 7 Alabama 2010-11 8071.134## 8 Alabama 2011-12 8451.902## 9 Alabama 2012-13 9098.069## 10 Alabama 2013-14 9358.929## # … with 590 more rows58 / 81
Compute summaries
annual_means <- tuition %>% pivot_longer(`2004-05`:`2015-16`, names_to = "year", values_to = "avg_tuition") %>% group_by(year) %>% summarize(mean_tuition = mean(avg_tuition))annual_means## # A tibble: 12 x 2## year mean_tuition## * <chr> <dbl>## 1 2004-05 6409.564## 2 2005-06 6654.177## 3 2006-07 6809.914## 4 2007-08 7085.881## 5 2008-09 7156.560## 6 2009-10 7761.810## 7 2010-11 8228.834## 8 2011-12 8539.115## 9 2012-13 8842.357## 10 2013-14 8947.938## 11 2014-15 9037.357## 12 2015-16 9317.63359 / 81
Grouped points
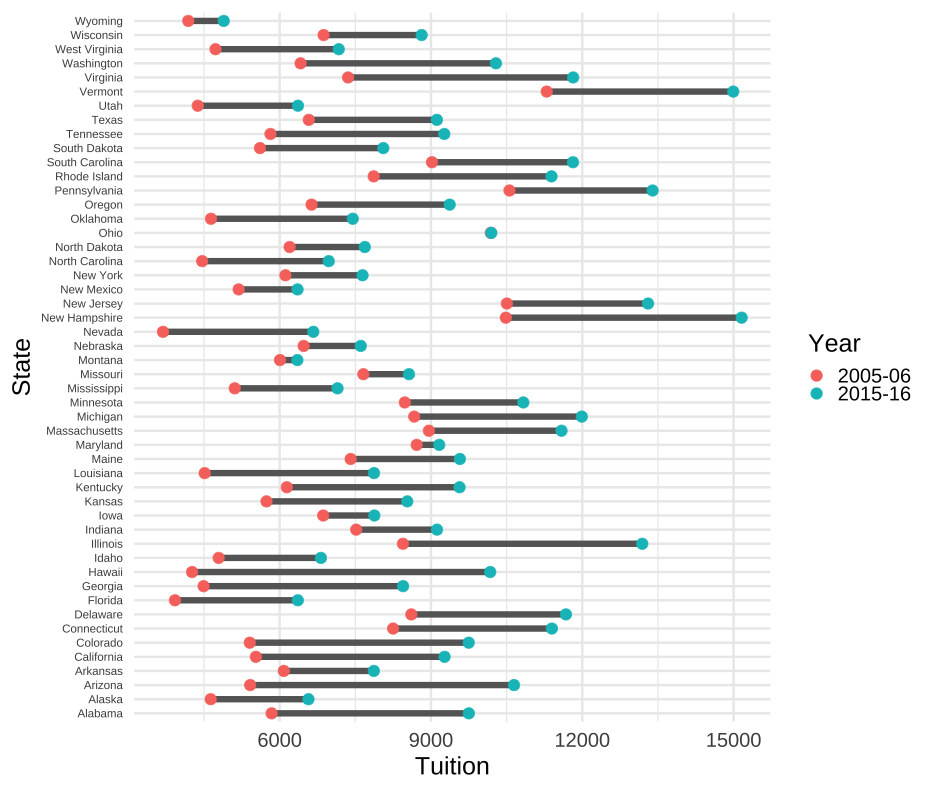
Show change in tuition from 05-06 to 2015-16
tuition %>% select(State, `2005-06`, `2015-16`)## # A tibble: 50 x 3## State `2005-06` `2015-16`## <chr> <dbl> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 5840.550 9751.101## 2 Alaska 4632.623 6571.340## 3 Arizona 5415.516 10646.28 ## 4 Arkansas 6082.379 7867.297## 5 California 5527.881 9269.844## 6 Colorado 5406.967 9748.188## 7 Connecticut 8249.074 11397.34 ## 8 Delaware 8610.597 11676.22 ## 9 Florida 3924.234 6360.159## 10 Georgia 4492.167 8446.961## # … with 40 more rows64 / 81
lt <- tuition %>% select(State, `2005-06`, `2015-16`) %>% pivot_longer(`2005-06`:`2015-16`, names_to = "Year", values_to = "Tuition")lt## # A tibble: 100 x 3## State Year Tuition## <chr> <chr> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 2005-06 5840.550## 2 Alabama 2015-16 9751.101## 3 Alaska 2005-06 4632.623## 4 Alaska 2015-16 6571.340## 5 Arizona 2005-06 5415.516## 6 Arizona 2015-16 10646.28 ## 7 Arkansas 2005-06 6082.379## 8 Arkansas 2015-16 7867.297## 9 California 2005-06 5527.881## 10 California 2015-16 9269.844## # … with 90 more rows65 / 81
Extensions
I know we're probably running short on time, but we definitely would want to keep going here:
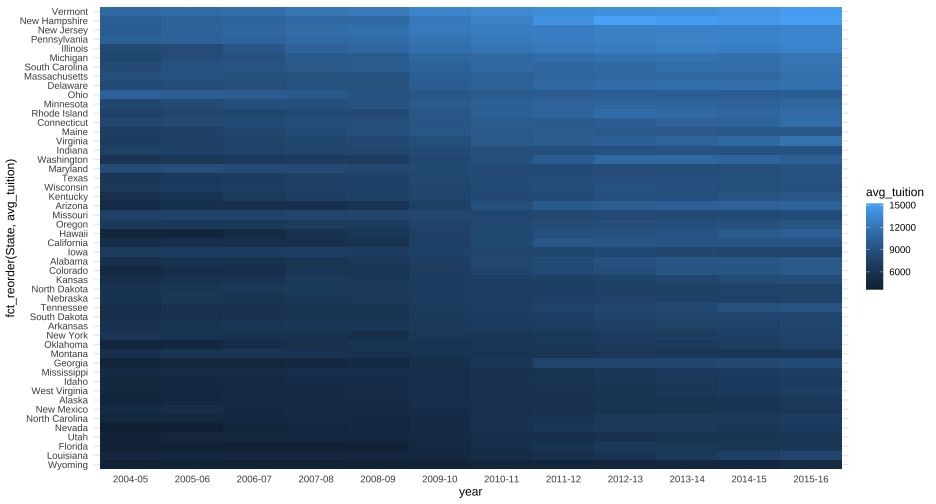
Order states according to something more meaningful (starting tuition, ending tuition, or difference in tuition)
Meaningful title, e.g., "Change in average tuition over a decade"
Consider better color scheme for points
68 / 81
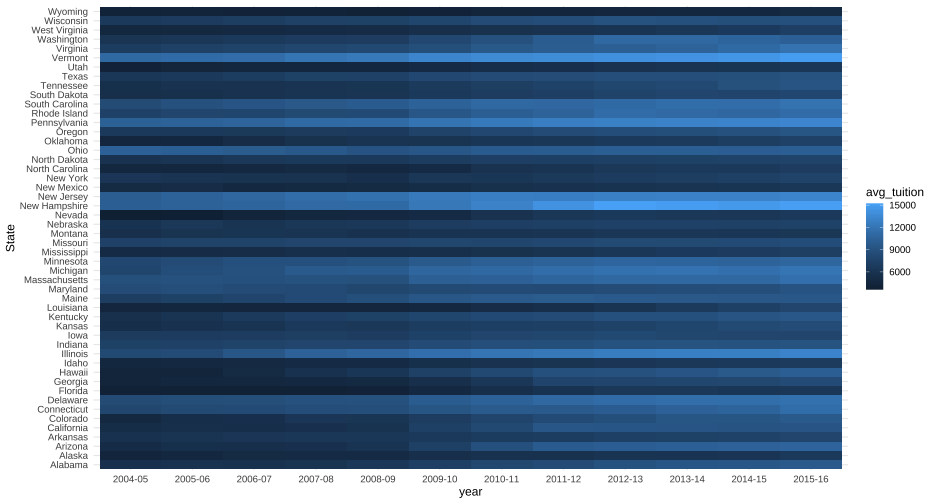
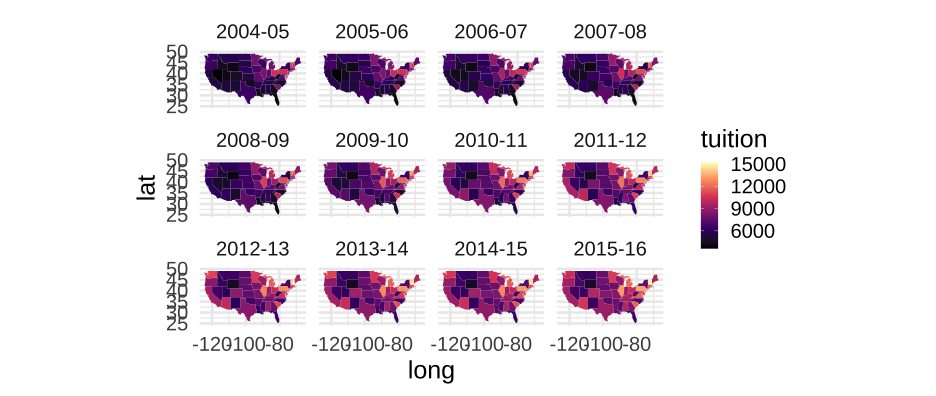
Let's back up a bit
- Lets go back to our full data, but in a format that we can have a
yearvariable.
tuition_l <- tuition %>% pivot_longer(-State, names_to = "year", values_to = "avg_tuition") tuition_l## # A tibble: 600 x 3## State year avg_tuition## <chr> <chr> <dbl>## 1 Alabama 2004-05 5682.838## 2 Alabama 2005-06 5840.550## 3 Alabama 2006-07 5753.496## 4 Alabama 2007-08 6008.169## 5 Alabama 2008-09 6475.092## 6 Alabama 2009-10 7188.954## 7 Alabama 2010-11 8071.134## 8 Alabama 2011-12 8451.902## 9 Alabama 2012-13 9098.069## 10 Alabama 2013-14 9358.929## # … with 590 more rows69 / 81
Join it
Obviously we'll talk more about joins later
tuition <- tuition %>% mutate(State = tolower(State))states <- left_join(state_data, tuition)head(states)## long lat group order State subregion 2004-05 2005-06 2006-07## 1 -87.46201 30.38968 1 1 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 2 -87.48493 30.37249 1 2 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 3 -87.52503 30.37249 1 3 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 4 -87.53076 30.33239 1 4 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 5 -87.57087 30.32665 1 5 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 6 -87.58806 30.32665 1 6 alabama <NA> 5682.838 5840.55 5753.496## 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15## 1 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 2 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 3 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 4 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 5 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 6 6008.169 6475.092 7188.954 8071.134 8451.902 9098.069 9358.929 9496.084## 2015-16## 1 9751.101## 2 9751.101## 3 9751.101## 4 9751.101## 5 9751.101## 6 9751.10175 / 81
Rearrange
states <- states %>% gather(year, tuition, `2004-05`:`2015-16`)head(states)## long lat group order State subregion year tuition## 1 -87.46201 30.38968 1 1 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.838## 2 -87.48493 30.37249 1 2 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.838## 3 -87.52503 30.37249 1 3 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.838## 4 -87.53076 30.33239 1 4 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.838## 5 -87.57087 30.32665 1 5 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.838## 6 -87.58806 30.32665 1 6 alabama <NA> 2004-05 5682.83876 / 81
Wrapping up
- We've got a ways to go - today was just an introduction
- The geographic part in particular was too fast, and we'll talk about better ways later (note that Alaska/Hawaii were not even included)
- We basically didn't talk about multivariate data (not even scatter plots)
- Other types of plots will be embedded within the topics later in the class
80 / 81